Reducing Overhead with Cuda Graph
By MTC Team ·Cuda Graph optimizes operations by packaging kernel launches, Tensor allocations, and similar tasks into a computational graph. This graph allows for direct replay of operations, significantly reducing the overhead of repeated execution. While such overhead is negligible during the computation-intensive prefill phase, it becomes more pronounced during the decode phase.
Meta-Llama-3-8B, bs=1, avg input length=1024
| Metric | Cuda Graph Enabled | Cuda Graph Disabled |
|---|---|---|
| Average Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.007046271026128699 | 0.023914787294611894 |
| Standard Deviation of Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.0009547402935623012 | 0.002686781278630856 |
Meta-Llama-3-8B, bs=64, avg input length=1024
| Metric | Cuda Graph Enabled | Cuda Graph Disabled |
|---|---|---|
| Average Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.03932000270337561 | 0.04153610316232362 |
| Standard Deviation of Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.014964249853381923 | 0.01310065607528607 |
Meta-Llama-3-8B, bs=128, avg input length=1024
| Metric | Cuda Graph Enabled | Cuda Graph Disabled |
|---|---|---|
| Average Decode Time (seconds) | 0.011849923196348719 | 0.03835266020430338 |
| Standard Deviation of Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.001037695231416684 | 0.0019032099654288915 |
DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat, bs=2, avg input length=10240
| Metric | Cuda Graph Enabled | Cuda Graph Disabled |
|---|---|---|
| Average Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.01640251212363981 | 0.04074279815826976 |
| Standard Deviation of Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.0025374513456306344 | 0.0018364576276859595 |
DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat, bs=20, avg input length=10240
| Metric | Cuda Graph Enabled | Cuda Graph Disabled |
|---|---|---|
| Average Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.01640251212363981 | 0.04074279815826976 |
| Standard Deviation of Single-Step Decode Time (seconds) | 0.0025374513456306344 | 0.0018364576276859595 |
For the Llama-3 model, with the prefix cache feature disabled, the results in the table (average input length of 1024, variance of 256, maximum length of 2048, output equal to input, 200 samples) demonstrate that enabling Cuda Graph (with a maximum total length of 4096) accelerates the decoding phase. The performance improvement is more pronounced with smaller batch sizes, and slightly less effective with larger batch sizes.
In the case of DeepSeek-V2, even with larger batches (average input length of 10240, variance of 2560, maximum length of 128000, and the output length equal to the input one, 20 samples in total), enabling Cuda Graph still results in a significant speedup during the decoding phase.
The original kernel allocated thread blocks based on the number of attention heads and batch size. However, this design caused load imbalances in thread blocks when processing batches of uneven lengths, negatively affecting performance. To address this, LightLLM redesigned the Decoding kernel for Cuda Graph using the concept of Virtual Stream Processors (VSM). The issue with the previous kernel was the dynamic change in request lengths, which caused the intermediate memory size to vary. In the new design, the number of thread blocks (Grid Size) is fixed, and the context of each request is divided into fixed-size blocks. Each thread block iterates over all blocks, translating the dynamically changing lengths into a fixed number of iterations, ensuring that intermediate memory usage depends only on batch size, eliminating the need for pre-allocated memory. Additionally, the fixed-size blocks ensure that each thread block’s load is nearly balanced, improving performance when handling batches of uneven lengths. Testing of the new DeepSeekV2 Decoding kernel showed that the redesigned kernel significantly outperforms the previous design in decoding speed for longer inputs, even with the same batch size and sequence lengths.
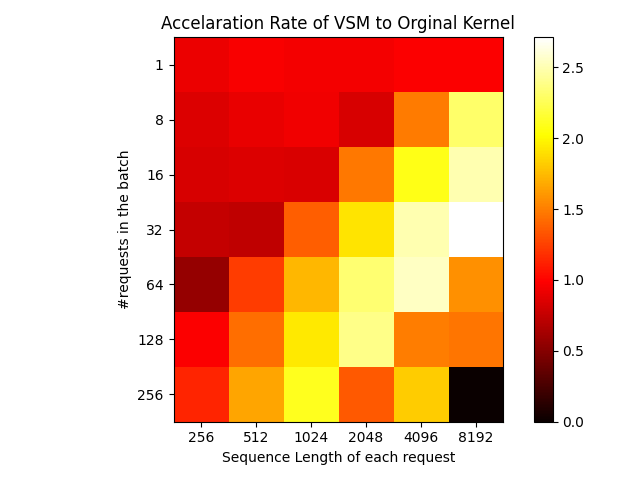
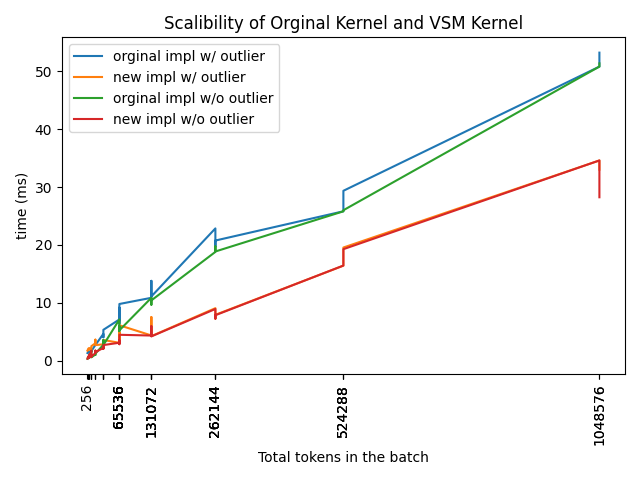
We also evaluated the scalability of the new kernel against the original implementation. The test batch consisted of 128 requests of uniform length, ranging from 256 to 8192, with outlier requests set to 8k length. The results showed that the new kernel performed better overall, with minimal impact from outlier requests (which are significantly longer than the average length), making it more stable compared to the original kernel.
Experimental Environment:
GPU: Single NVIDIA H800
GPU Driver Version: 535.86.10
CUDA Version: 12.2
CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6448Y
Python Version: 3.9
PyTorch Version: 2.4.0
LightLLM Commit ID: 6ede09e14a839314ff4991c504030caa412a4fc6
vllm Version: 0.6.6.post1
Experimental Setup:
Meta-Llama-3-8B
Maximum Total Tokens: 256k
Quantization Type: ao-w4a16-128
Parallelism: tp=1
Input Configuration:
Distribution: Normal
Average Input Length: 1024
Variance: 256
Maximum Length: 2048
Output: Same as Input
Batch Sizes (bs): 1, 64, 128
DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat
Maximum Total Tokens: 256k
Parallelism: tp=1
Input Configuration:
Distribution: Normal
Average Input Length: 10240
Variance: 2560
Maximum Length: 128000
Output: Same as Input
Batch Sizes (bs): 2, 20